*This is a translation from Ukrainian of the article published a week ago*
I don’t know where you are, but here it’s cold winter and everyone rushes home every evening to warm up in the comfort of a fireplace or electric heater. At the same time somewhere far away, probably thousands kilometers from you, in the cold ocean water live interesting creatures who don’t have any chance to warm up, but also don’t need it, because they are cold-blooded. I’m talking about the tasty biters that go sideways – crabs. I hope I have sufficiently prepared you for the next bold statement with my introductory speech. Sit down if you are standing. Several species of crustaceans independently evolve into crabs!

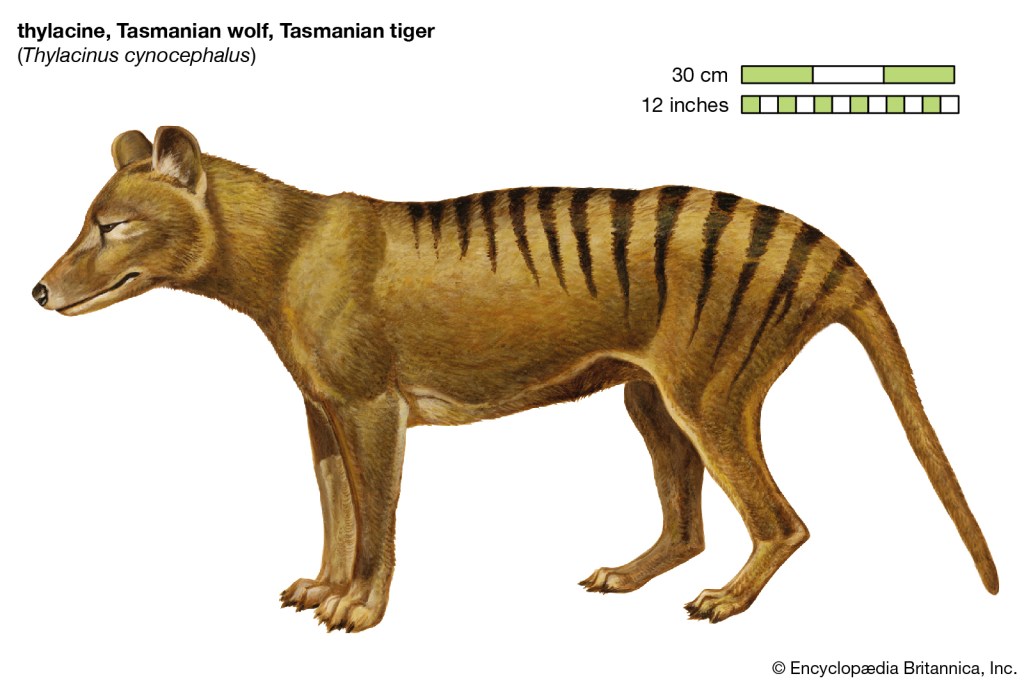
This process is an example of convergent evolution, the phenomenon when unrelated species of animals, or rather living organisms in general, under the influence of similar environment develop similar functions, resulting in similar morphological features. A striking example of convergent evolution is the development of wings in unrelated species such as bats, birds and pterosaurs, one of which is the pterodactyl. Another interesting example is the thylacine, or Tasmanian wolf. This animal, which unfortunately became extinct in the early twentieth century, is a marsupial. It lived in Australia, Tasmania, and if I’m not mistaken New Guinea. It is similar in origin to the kangaroo, but occupies a free niche of the predator, and due to similar living conditions to wolves has a body structure, including paws, and especially noticeable – the jaws that are very similar to wolves or dogs. You can even find a video of the beginning of the century of thylacine in the zoo, where you can see the dog-like behavior of the animal.
However, back to our popular snacks – crustaceans. Scientists have called the process of evolution of different species of crustaceans into a form close to a crab carcinization. Except of real crabs, which belong to the infraorder Brachyura of Pleocymata suborder (other members of which are also crustaceans, lobsters, and shrimps), at least the following four animals evolved into a crab-like form independently.
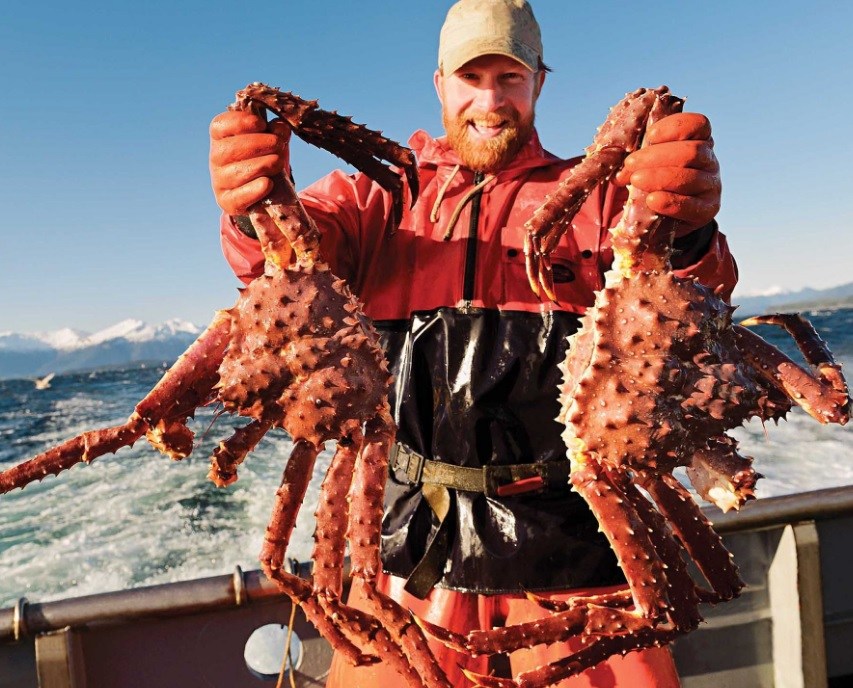

- King crabs. They differ from the real crabs by reduced last pair of limbs and an asymmetrical body structure. King crabs derive from hermit crabs, which have asymmetrical structure in order to be able to live in the empty shells of mollusks. Alaskan crab, one of the species of king crabs is a popular object of fishing. Legspan of these crabs reaches 1.8 meters.

2. Actual hermit crabs. The body of these crustaceans is not protected by shell, so they found their way to protect themselves from predators by finding empty shells of mollusks and using them as a shelter. As the body of these crabs grows during their lifetime, it cannot grow if the shell is too tight for it, so at some point they decide to change the shell to a larger one. In some places empty shells are in short supply, so if two crabs of the same size compete for one shell, they begin to fight, often to death. Crabs of different sizes are not competitors to each other, so they can coexist peacefully.
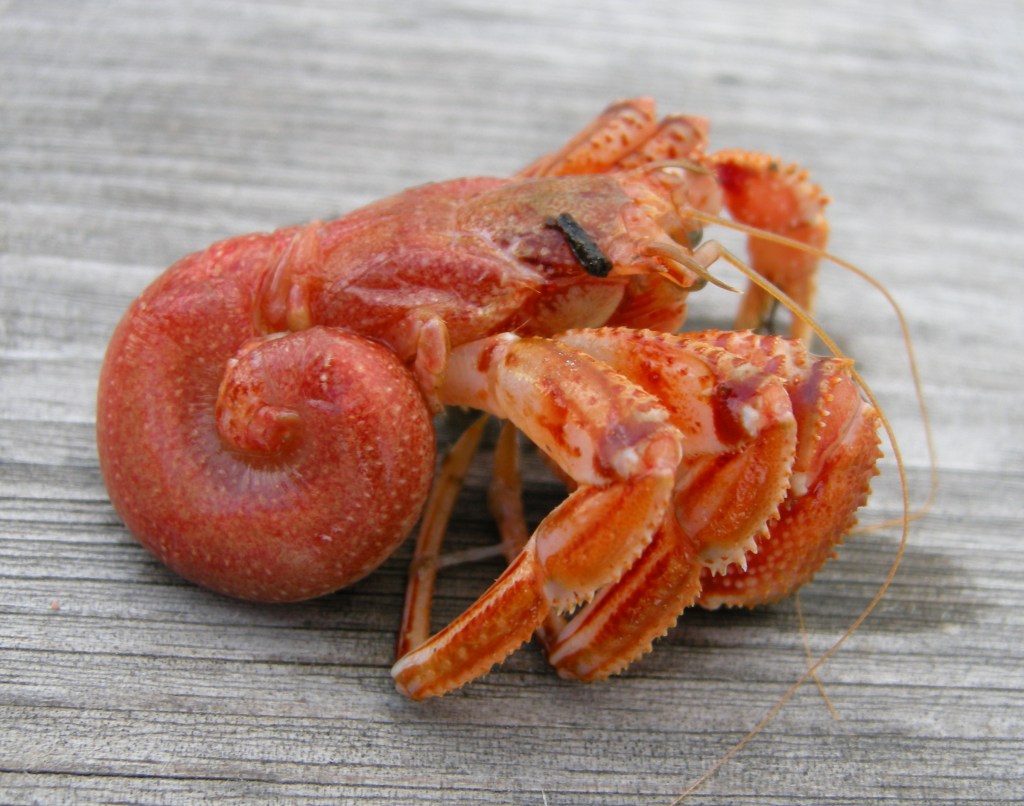

When a hermit crab looks for potential living space, it checks the volume of the new shell. In case the shell turns out to be too big he returns to his shell and starts waiting next to the shell that is too big. He is waiting for a crab bigger than him who also looks for a new shell. This waiting can last up to eight hours. When a larger crab comes and a new shell suits him/her, the waiting crab takes over the old shell of the larger crab. This way, up to twenty crabs of various sizes can group at the same place waiting for the biggest crab. As soon as the largest one occupies the new shell, the second largest occupies the old shell of the largest, the third largest occupies the old shell of the second, and so on.
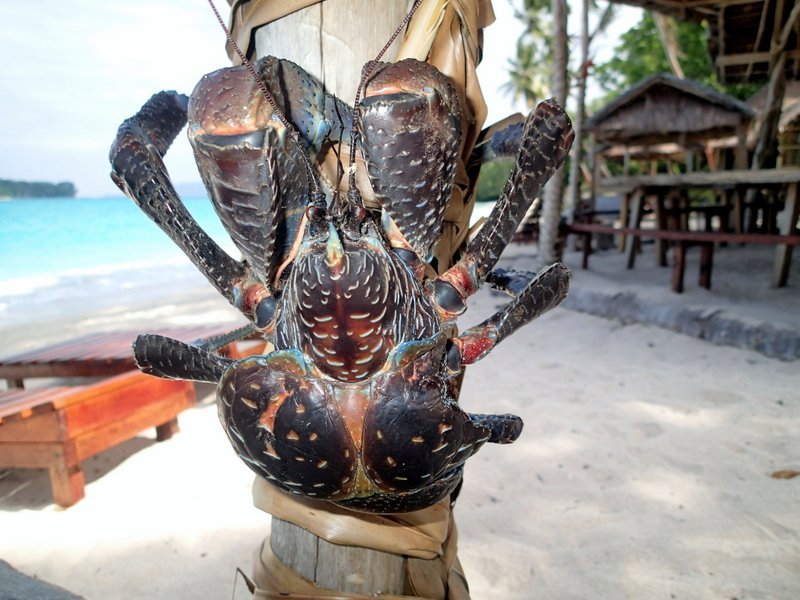

2A. The following animal which evolves into a crab is a relative of the hermit crab, the coconut crab. We count it as the same point, because together with a relative they evolved together till some point of time, until their paths diverged. Unlike its relative, it uses shells as a shelter only in childhood and adolescence, while adults live on shore of the tropical islands of the Indian and Pacific Oceans. The lifespan of these crabs is over 60 years, legspan up to one meter, weight 4-5kg. Coconut crabs are able to open and feed on coconuts, which however are not their main source of nutrition. They feed on everything – mollusks, fruits, leftovers from humans, insects. There are rumors that they also prey on rats and birds, I don’t know if it’s true, but at least there is a video on the Internet where a coconut crab successfully attacks some big bird like a seagull, find it, you won’t regret it.
3. Porcelain crab – a small animal about 15mm in size, which hides under rocks. Its claws are used only to defend the territory, but not for getting food, as it feeds on plankton. In case of encounters with predators trying to rescue they shed their legs, hence their name.
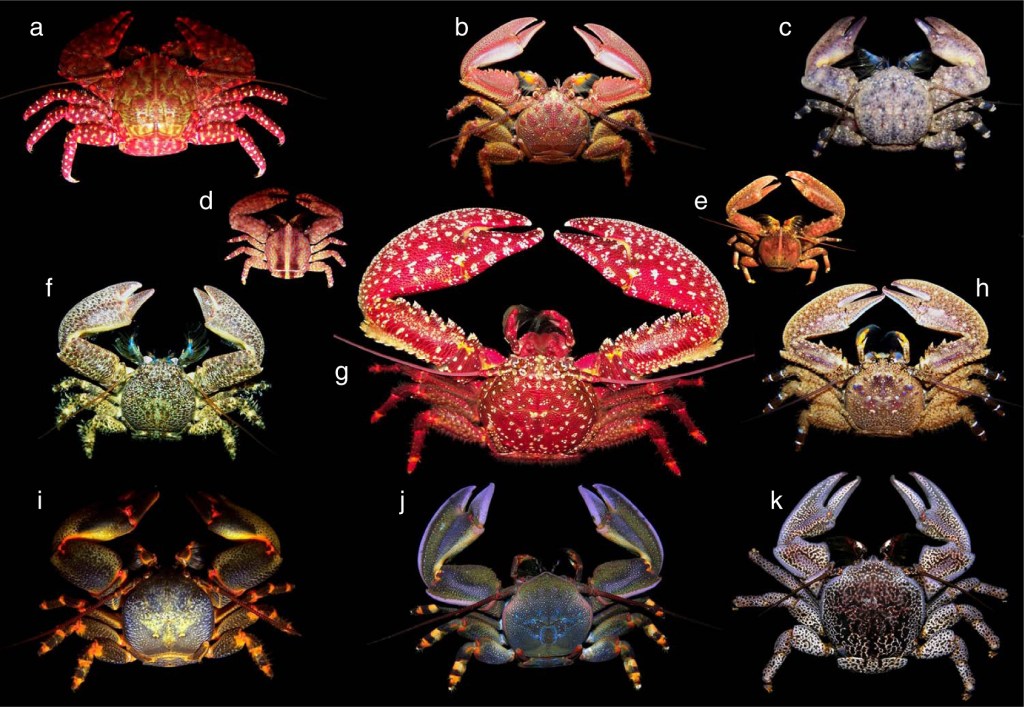

4. Hairy stone crab is also a small animal measuring 15-25 mm. These “crabs” live on the ocean rocks. Unlike other crabs, which as we have already understood are not even close relatives, these move slowly. They live on a part of the south coast of Australia.
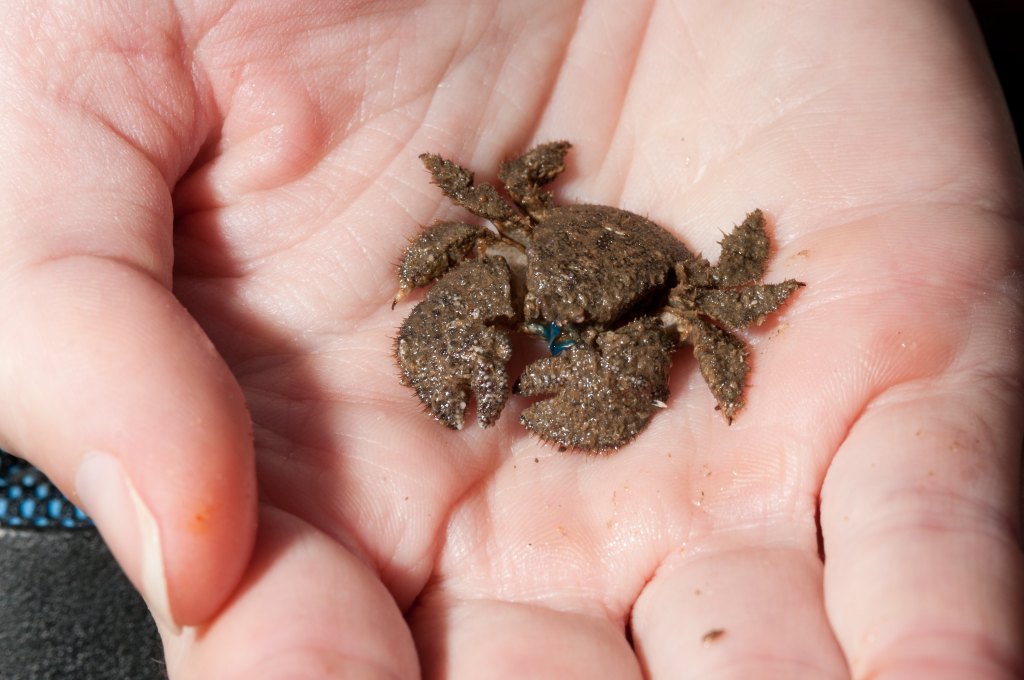

Bonus. Another animal that evolved into a crab before the real crab evolved into a crab and then became extinct is the Cyclida order. Existed from Carboniferous to the Cretaceous period. It seems to have occupied a similar ecological niche to modern crabs. The gills of this order are not similar to the gills of modern crustaceans.
For crustaceous creatures, they look so tantalizing without their shells.
LikeLike